Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI framework that enhances the capability of an LLM to provide answers relevant to a certain domain by referring to a private knowledge base before generating answers. Today, LLMs have fast become the primary source of answers for a wide range of questions that we have on a daily basis. While LLMs like ChatGPT, Gemini, Qwen, Anthropic etc can surprisingly provide information on a wide range of topics, LLMs are also prone to a common problem called Hallucination.
Hallucination is the term for the phenomenon where an LLM provides wrong or non sensical information or just plain makes us a response that has no logical basis. While with time, LLMs have become far more accurate than they use to be before, hallucinations still remain a common observation across the AI ecosystem. This is the reason why every LLM will have a disclaimer to not trust its answers blindly.
There are various reasons why LLMs are prone to hallucinations:
- Nature of Language Modeling: LLMs are trained to predict the next word in a sequence based on patterns in a massive dataset. They do not know any “facts” and just follow their algorithm to produce answers, which in some cases, could be incorrect.
- Lack of grounded knowledge: LLMs do not have access to real time database or up to date information about the world. In absence of this information, LLMs can sometime resort to “guessing” the answer or provide outdated response to the question.
- Training data limitation: LLMs provide answers on the basis of the data that they have been trained on. This data could have its own limitations (incomplete, outdated, incorrect) which prevents the LLM from knowing everything. Since all LLMs are trained on different datasets, they are prone to producing different hallucinations from each other.
- Overconfidence in output: LLMs are designed to provide fluent answers in as short time as possible. This may lead to LLM trying to fill in gaps for areas not answered by its training data, and provide incorrect response.
- Incomplete or unclear prompt: If the prompt provided lacks clear requirement, the LLM would try to assume the missing information and can result in unexpected response.

RAG aims to tackle the problem of hallucination by providing a set of relevant and accurate documents for the LLM to refer to, before generating the answer. The added piece here is called Knowledge Base. With access to knowledge base, the LLM now has more accurate information at its disposal which helps create relevant answers. This process is divided into two parts:
Retrieval: When the user asks a question, the RAG system first searches internal or external knowledge base (pdf files, database, websites etc) to find most relevant information.
Generation: The information is then packed with the user query and sent to the LLM to generate answer based on this information.
The generation capability of the LLM is now augmented through the information that was retrieved from the knowledge base. Hence this is called Retrieval-Augmented Generation system.
Architecture of RAG
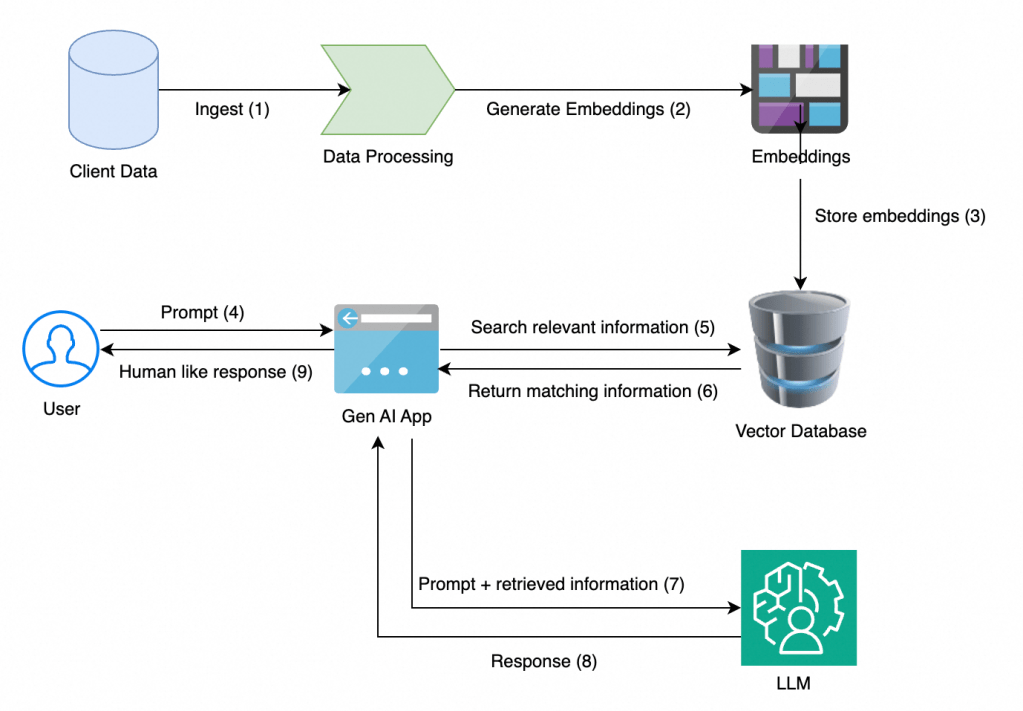
Client data processing and storage: Raw data needs to be processed and stored in order to build a knowledge base. This could include pdf, word, excel files, database, scraped pages from websites. All this information is processed and stored (eg: OSS from Alibaba Cloud).
Embedding: In order for AI systems to understand any data, it needs to converted from its existing form (text, audio, video etc) to a numerical form called vectors. Vectors is the language of AI and embedding models carry the task of converting data to vectors. Popular embedding models include OpenAI, Cohere, Qwen-Embedding etc.
At a high level, an embedding model takes a piece of information, like a word or a sentence, and maps it to a point in a multi-dimensional space. The key principle is that items with similar meanings are placed closer together in this space. For example, the embedding for “dog” and “puppy” would be closer to each other than the embedding for “bicycle.”

Vector DB: After the data is converted to vectors by embedding model, the vectors need to be stored in a database. This database is called Vector DB. This database also searches the closest vectors to the input prompt and provides the most relevant matches also known as Top-P. This is called vector search. Popular vectorDB are Milvis, Pinecone, AnalyticDB for PGSQL etc. The formation of vectorDB signifies the completion of setup of a knowledge base.
LLM: An LLM model receives vectors for prompt and the matching information received from VectorDB and generates response. Popular LLMs are GPT, Qwen, Anthropic etc.
GenAI App: This is the web deployment of front end application that the user interacts with.
RAG system on Alibaba Cloud
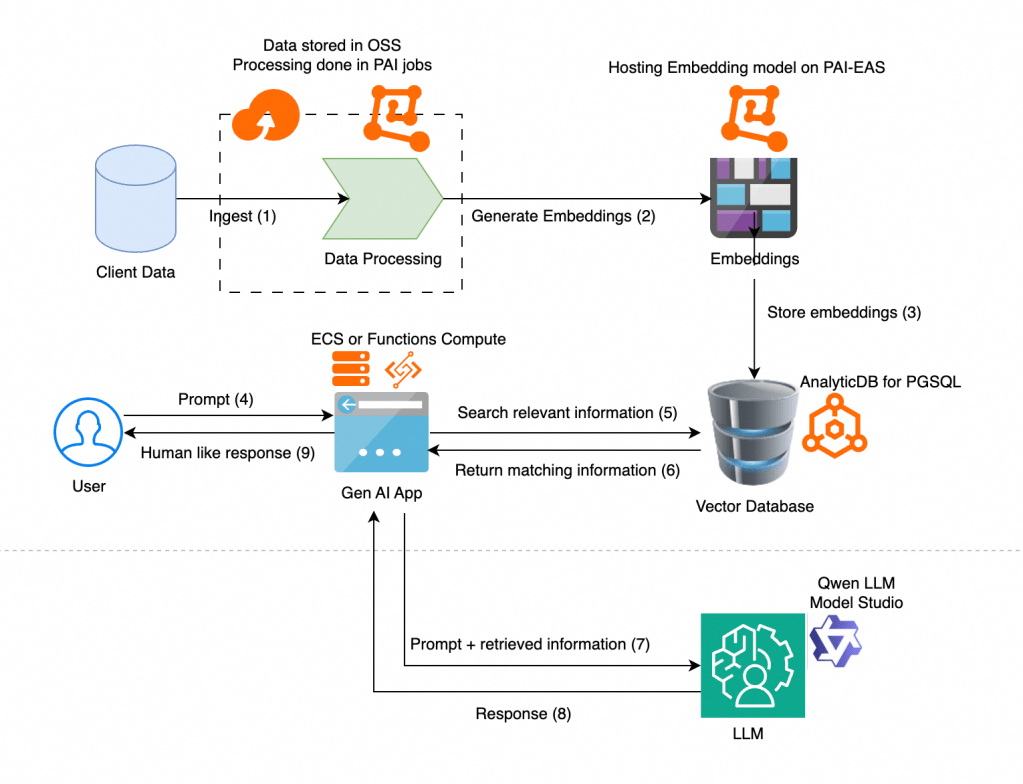
Ingest & Data Processing
- Original: Client Data -> Data Processing
- Alibaba Cloud:
- Data Ingestion: The client data (documents, files, etc.) would be stored in Object Storage Service (OSS). OSS provides a scalable and cost-effective solution for storing unstructured data.
- Data Processing: We would use Platform for AI (PAI) to run the data processing jobs. PAI offers a managed environment for building and running ML workflows. This is where we would perform tasks like document parsing, chunking, and cleaning.
Generate Embeddings
- Original: Data Processing -> Generate Embeddings
- Alibaba Cloud:
- Embedding Model: We can deploy an embedding model (like Qwen-Embeddings or an open-source one from Hugging Face or a proprietary model from DashScope) using PAI’s Elastic Algorithm Service (PAI-EAS). PAI-EAS allows us to deploy models as low-latency API endpoints, which our data processing job can call to convert text chunks into vectors.
Store Embeddings
- Original: Embeddings -> Vector Database
- Alibaba Cloud:
- Vector Database: The generated embeddings would be stored in ApsaraDB for AnalyticDB. It allows us to store both text chunks and their corresponding embeddings in one place.
Retrieval Flow
- Original: User Prompt -> Gen AI App -> Search Vector Database -> Return Matching Information
- Alibaba Cloud:
- User Prompt & Application Logic: The user’s prompt would be handled by our application, which could be a serverless function running on Function Compute or a service running on Elastic Compute Service (ECS). This application would call the PAI-EAS API to generate an embedding for the user’s query, then use this query embedding to search the vector database for the most relevant documents.
Generation Flow
- Original: Prompt + Retrieved Information -> LLM -> Response -> Gen AI App -> Human-like Response
- Alibaba Cloud:
- LLM: The application would send the combined prompt (original question + retrieved context) to a Large Language Model hosted on ModelStudio which provides Model-as-a-Service offering. Various editions of Qwen can be used as LLM here.
- Final Response: The final, grounded response from the LLM is sent back through your application to the user.
Building RAG with Model Studio and Dify in a few clicks
While we can build the entire component of an RAG on Alibaba Cloud as described above, we can also take advantage of platforms like Dify to quickly build RAG in a few clicks. Dify is an open-source platform designed to help developers build and operate AI applications. It provides a visual interface for creating and managing different types of AI workflows, such as chatbots, RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) systems, and agents.
Dify makes the process of creating RAG easier by hiding the complexity behind creating and managing the knowledge base through handling of embedding automatically. The documents added to knowledge base are automatically embedded and stored in a vector DB managed by Dify. This makes the entire process of creation of RAG much simpler. Lets do that now:
For this article, we have chosen the cloud version of Dify. For an enterprise deployment, Dify can also be hosted in Alibaba Cloud Compute Nest or DMS or on ECS server.
Once an account is created on Dify (cloud.dify.ai), we connect the platform to Alibaba Model Studio so we can use Qwen as the underlying LLM. Alibaba Model Studio provides access to the entire family of Qwen LLM models. To connect Dify with model studio, we add Tongyi (Qwen formal name) as a model provider.
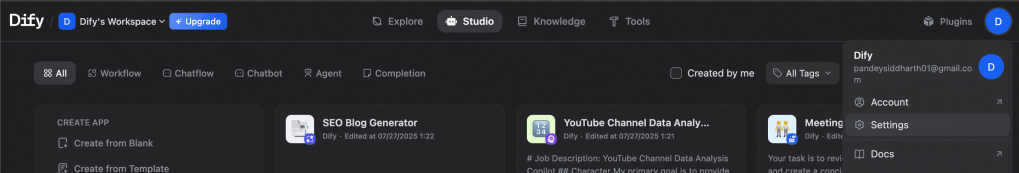
In settings, go to Model Provider, and scroll down to find Tongyi. Click on Install
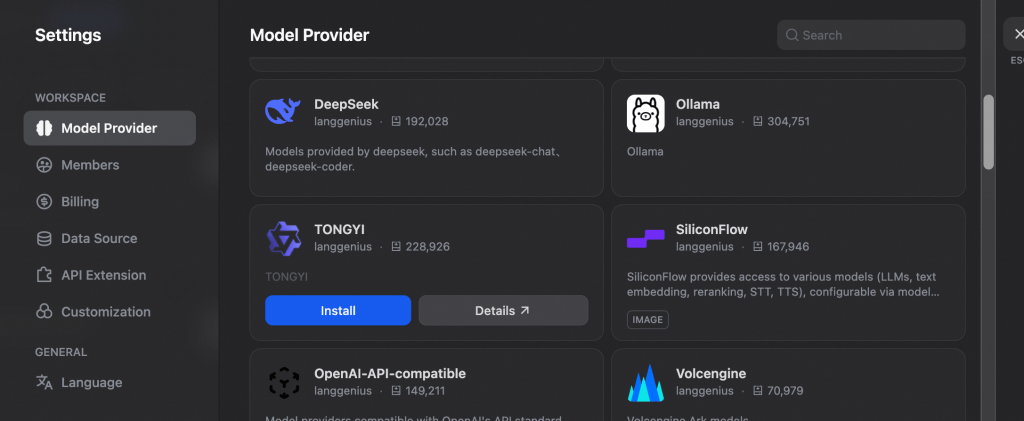
Once Tongyi is installed, we can connect it to Alibaba Model Studio by providing API KEY from Model Studio. For this, go to your Alibaba Cloud console–>Model Studio–>Click on settings icon on top right–>All API Keys–>Create API Key.
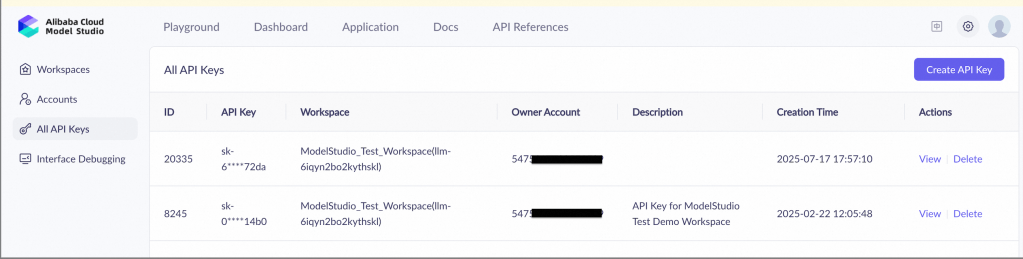
This API key can be setup in Dify once Tongyi installation is completed. Click on Setup and paste the API key to complete the model provider connection.
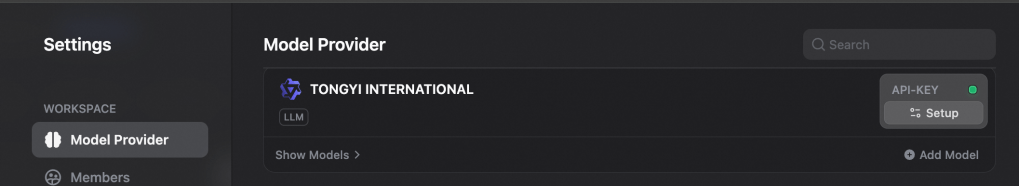
Now we can start creating the RAG application. Go to Dify home page and click on Create from Template. For this article, we will create a simple RAG chatbot application.
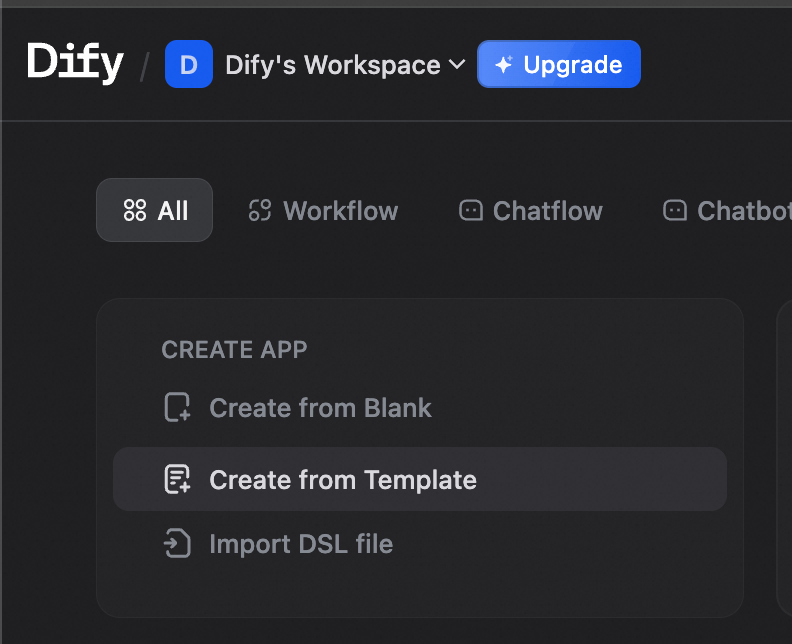
Search for “chatbot” and select Knowledge Retrieval + Chatbot template.
Note on The Furrville Pet Studio:
Furrville Pet Studio is an all in one pet grooming salon in Singapore, which is run by one of my friends. We take example of this business and build an RAG system for them along with a chatbot that users can interact with in order to understand more about Furrville.
Once you have selected the template, we see the default workflow on the designed page. The workflow consists of a start node, a knowledge base, an LLM and an answer node.
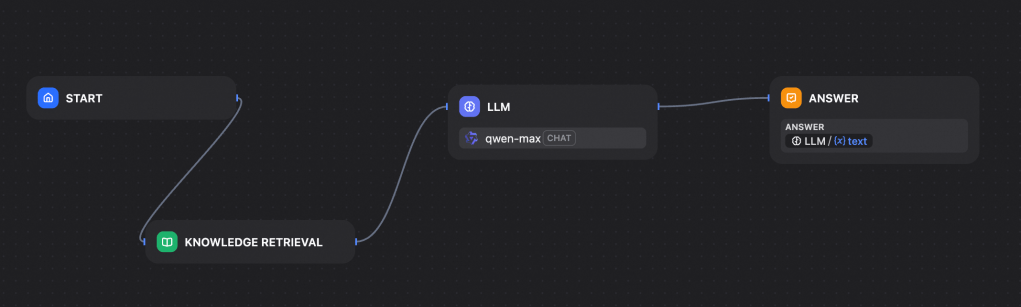
Here I have already selected qwen-max as my model. We can select the model by clicking on LLM tab and selecting the desired model from the drop down. Since we have connected Dify with Model Studio through API KEY, all models of Qwen hosted in Model Studio will now be visible in the selection drop down.
Now, we need to create a knowledge base that Qwen can refer to, in order to prepare answers to user queries. To do this, we click on Knowledge tab on top of the page.
Click on Create Knowledge. Here, we can add data in various ways. We can add pdf, excel, word files etc, or upload a notion file. In our case, we want to sync from furrville official website to get details on their services. This can be done by scraping web pages of the website. Web scraping providers like Jina Reader and Firecrawl are already embedded in Dify. We can give the URL of the website and the pages will be scraped and added to the knowledge base.
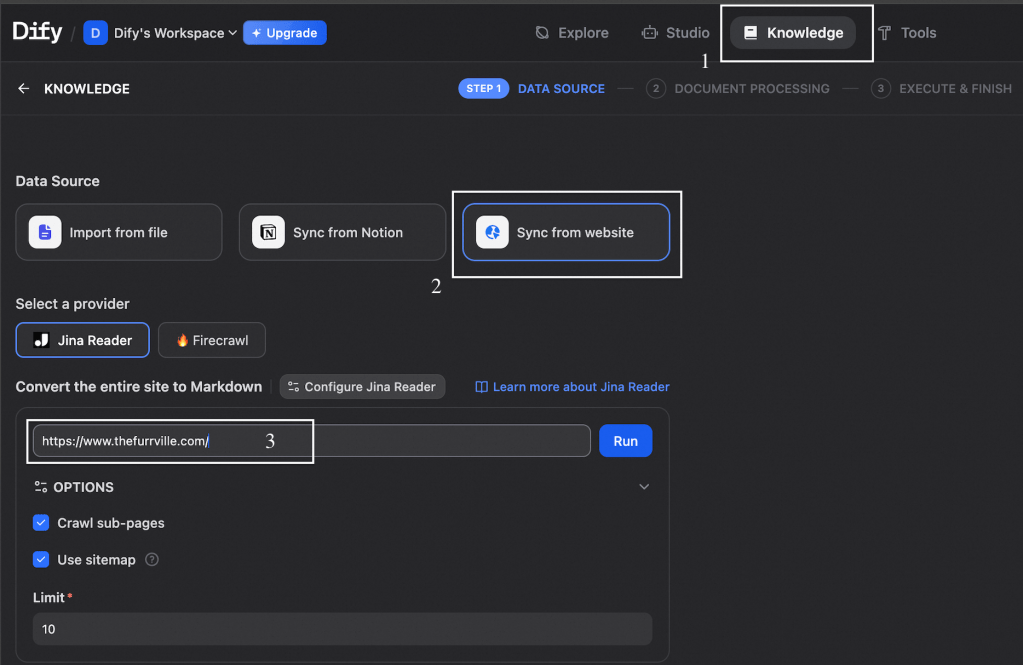
After the scraping and indexing is completed by Jina Reader, I have scraped files added in my knowledge base. Now my knowledge base is ready to be linked to the LLM to form an RAG system.
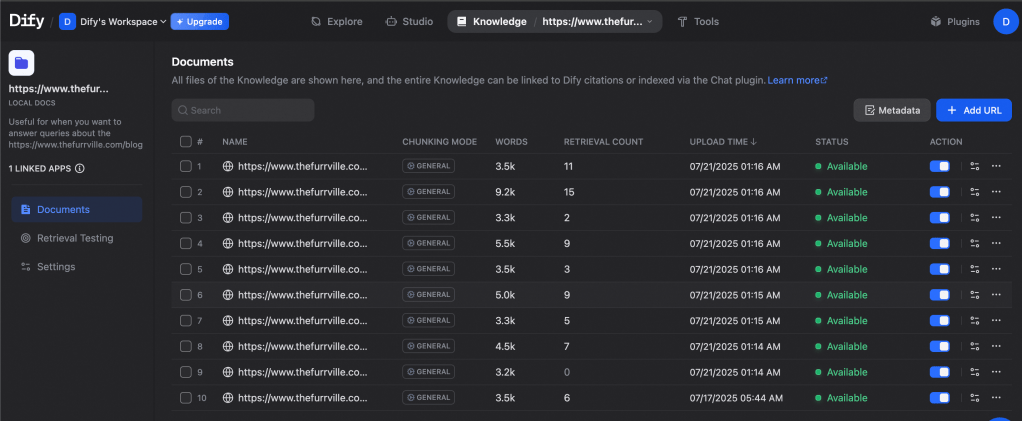
We go back to the workflow page by clicking on Studio on the top panel and selecting our workflow. Here we click on Knowledge Base workflow element and add the knowledge base that we just created.
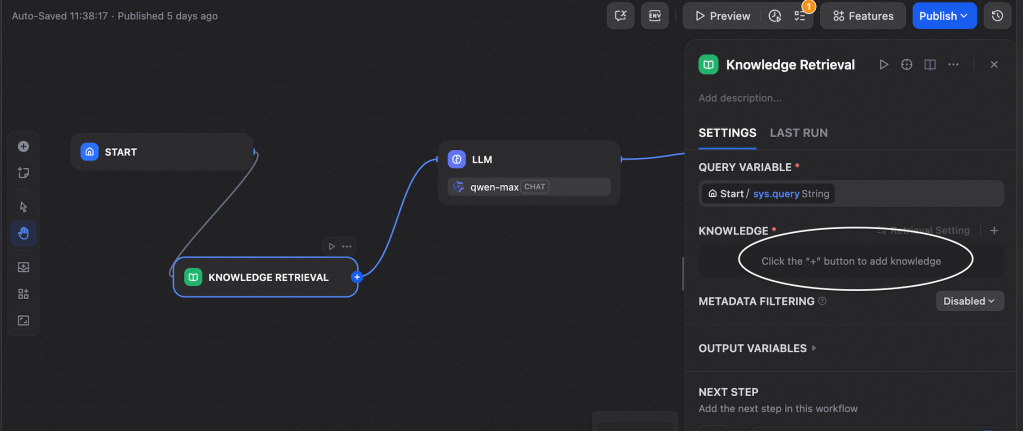
Once the knowledge base is configured, we configure the LLM element. Here we select the desired model from Qwen family. Then we select context as result under Knowledge Retrieval. Here we are telling the model that it needs to refer to the result from knowledge base as the context for creating answers. Now we will provide description to the chatbot on its role and also ask it to refer to the context we just set.
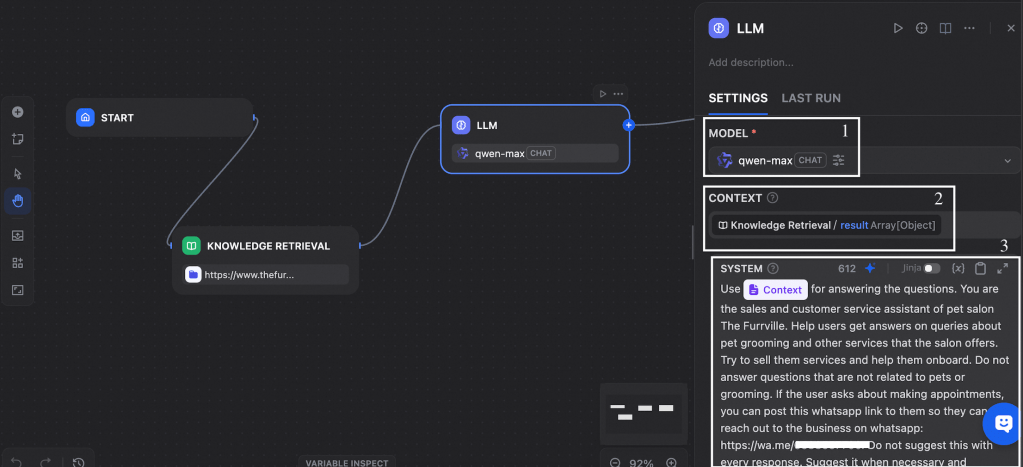
Our chatbot is ready now. We can test it by clicking on Publish and selecting Run App, which will launch a web application chatbot for testing the RAG. You can now ask the chatbot about various services at Furrville salon. The chatbot will refer to the knowledge base, get the relevant information and present to you in form of multi-round chat.
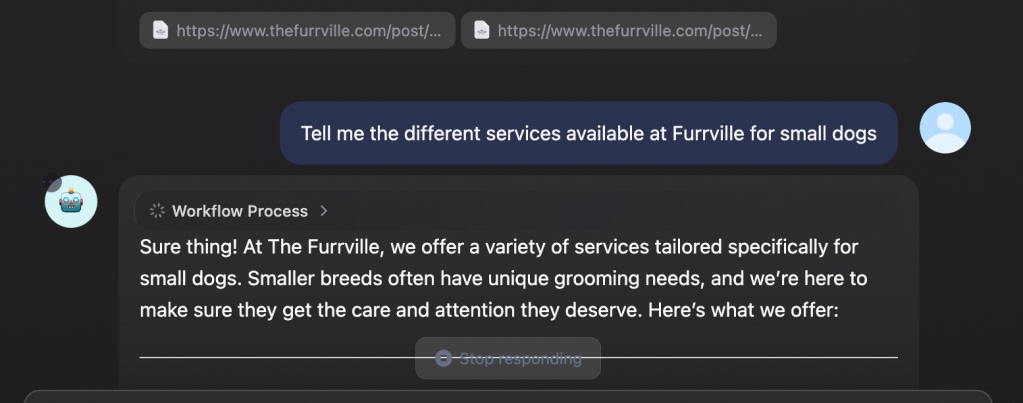
Thats it! Our chatbot is up and running. Once the testing is completed, we can use the chatbot in production by embedding it into the actual furrville website or by exposing the chatbot through APIs.
There you go folks. Creating a chatbot with Alibaba Cloud Model Studio and Dify was a simple and short task. You can further control each element of this deployment by hosting it in Alibaba Cloud as we saw in the architecture diagram above. You can use the RAG as a valuable component of your application, or if the business need arises, convert this RAG into an agent by enabling access to tools and adding dynamic decision making capabilities. Let’s uncover that in another blog soon!